- Components - Spare Parts
- Engine Power
- Light aircraft electric motor
- FAULHABER Drive Systems
- Company
- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
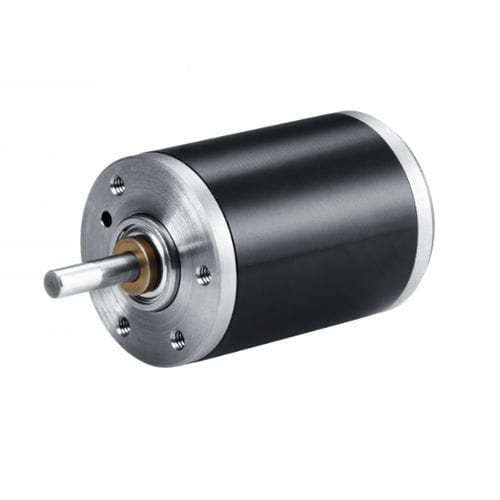
Light aircraft electric motor AM seriestwo-phase stepper
Add to favorites
Compare this product
fo_shop_gate_exact_title
Characteristics
- Application
- for light aircraft
- Type
- two-phase stepper
Description
Diameter:
8 ... 32 mm
Length:
13.8 ... 42 mm
Step angle (full step):
7.5 ... 18 °
Static torque rating:
0.65 ... 85 mNm
Two phase stepper motors with single magnets
The stepper motors of the FAULHABER AM family are ideal for positioning tasks that require high accuracy. They are characterized by a high holding torque and power density while keeping power consumption low. Even without power supply, they are able to hold their positions, which makes them the ideal choice of miniature stepper motors for battery-operated applications. Being available in various sizes and diameters and offering 20, 24 or 48 steps per revolution, the AM motors are very versatile and applicable to a vast variety of application areas.
The FAULHABER AM series can be combined with a wide selection of fitting controllers, encoders, gearheads and linear actuators, creating a powerful drive system for a broad range of positioning tasks. In laboratory automation, the miniature stepper motors are applied for moving and orientating samples during pipetting tasks, while in optics applications, they can be used, for example, for the positioning of moving stages in microscopes or scanning. Within satellites, the AM motor series can perform the precise positioning of antennas or solar panels.
Catalogs
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.